While coating the articles and job how the customer should know how much quantity will be used and the cost will be incurred. However, calculating powder coating cost can be a small task, we are going to show you how to calculate powder coating layer coverage and how to gather the information necessary to give a right accurate prediction of cost per square meter, foot, inches.
We start calculating coverage costs, these are the values that you will need to know:
A. Powder Specific Gravity: - To Determine Specific Gravity of powder paint by Pycnometer method.
Equipment: -
Theory: - The Pycnometer method can be used for determination of the specific gravity of powder particles. The specific gravity of powder particles is determined using the relation. Clean the pycnometer with methyl ethyl ketone (MEK).
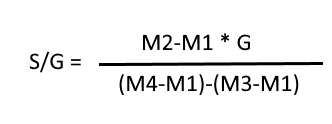
Where M1= mass of empty Pycnometer
M2= mass of the Pycnometer with powder
M3= mass of Pycnometer and powder and kerosene oil
M4= mass of Pycnometer filled with water only.
G= Specific gravity of kerosene oil(0.096)
B. Depend on Paint Finish: - The coverage of powder paints depends on powder colour finish. Like a smooth, metallic, structure, and texture, antique will have different coverage. For example,structure powder coating pattern two type one a small pattern and another bold pattern. Small patterns come 70-80 microns but bold patterns come 100-120 micron. So both product coverage found different.
C. Powder Cost: - The powder coating paints per Kg cost depends on coverage. Customers and salesmen of manufacturing groups should know one-kilogram price.
D. Transfer Efficiency: -Transfer Efficiency is the ratio of the powder coating actually deposited on the substrate as compared to the amount directed at the parts to be coated.Transfer efficiency is a really good measure of how well your guns are operating and how much a powder transfers, charges and is stuck to a part. It can be determined by measuring gun output at given conditions (feed voltage and current, Air pressure). Since transfer efficiency cannot be achieved 100% at various coating plants hence coaters install recycle systems in their process. The ratio of mixing of reclame powder and fresh powder depends on the application. Normally it is recommended to mix in 80:20 ratio Fresh/Reclaim.
Whether you calculate paint coating transfer efficiency by the weight method or the volume method, the variance in the figures gives you an idea of how efficient or inefficient your coating process reality. Determining it can be accomplished with a clean booth end of the spray gun and triggering it for 30 seconds. Weight of the net contents of powder and you can calculate approximate the rate of powder delivery per minute. To determine deposition, weight a part before coating and after it is coated. Then divide the amount deposited by the amount of powder estimated to exit the gun.
Calculate powder transfer efficiency equation: -
Transfer Efficiency % = Deposited Powder on part (Grams) ÷ Existing Powder Spray Gun (Grams)
Existing Powder Spray Gun (Grams) = Output Rate per Minute (Grams) × Total time
This powder transfer Efficiency depends on two types of efficiency. Details below
First Pass Transfer Efficiency: -This First Pass efficiency describes the percentage of virgin (Fresh) powder deposited on a substrate. If overspray is dropdown powder and reintroduced after filter into the feed hopper, after that the more generic term first pass transfer efficiency applied. Transfer efficiency tends to drop somewhat as more reclaim is added because the “good particles” (>10 microns, <100 microns) transfer efficiency at the high rate, the concentration of the low transfer efficiency efficient particles (<10 microns, >100 microns) increases as reclaim is introduced.
Transfer Efficiency Variable Table: -
|
Transfer Efficiency Variable |
Efficiency Impact |
Ease of change |
|---|---|---|
|
Gun to part distance |
10 |
4 |
|
Gun voltage |
10 |
5 |
|
Powder output |
8 |
3 |
|
Recovery System |
9 |
5 |
|
Air Pressure |
10 |
3 |
|
Powder Cloud |
7 |
4 |
|
Article size, Shape, & complexity |
8 |
10 |
|
Grounding, Hanger cleaning |
10 |
4 |
|
Line speed |
5 |
5 |
|
Film thickness |
6 |
5 |
|
Virgin to recycle ratio |
10 |
4 |
|
Powder particle size |
5 |
5 |
→ 1(Low Impact) & 10(High Impact) / → 1(Easiest) & 10 (Most difficult)
System Efficiency: -Application System efficiency % is mostly more important than transfer efficiency. This measurement captures the ratio of powder used versus powder deposited on the substrate. It takes into account losses encountered anywhere within the finish system. Things like coating on DP box, Fan blade and racks, powder hung up in reclaim filters and contaminated powder that was disposed are measured. Calculating system efficiency % takes a lot of time and data. It’s best to track the amount of powder coating used, the approximate amount of powder volume applied to parts and the number of parts produced.
Best Transfer efficiency depends in application below pointes: -
Better supervision and training will also help your paint coating applicators to know their equipment. Painters and coaters greatly improve this transfer efficiency when they know their tools and feel comfortable with them. One of the first pass efficiency steps to master is knowing the proper spray gun set-up.
E. Dry Film Thickness: ---- Powder coating thickness directly correlated to powder coating coverage. (1 kg powder how much square meter/Feet/Inches covered)
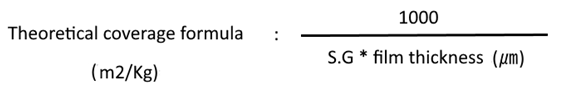
Coverage Table compare with film thickness or powder finish (This table theoretical based)
|
SG |
Film Thickness (Micron) |
Smooth (Square Meter/Kg) |
Film Thickness (Micron) |
Structure (Square Meter/Kg) |
Film Thickness (Micron) |
Texture (Square Meter/Kg) |
Film Thickness (Micron) |
Antique (Square Meter/Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1.65 |
50 |
12.10 |
80 |
7.57 |
60 |
10.10 |
100 |
6.06 |
|
1.70 |
50 |
11.76 |
80 |
7.35 |
60 |
9.80 |
100 |
5.88 |
|
1.75 |
50 |
11.42 |
80 |
7.14 |
60 |
9.50 |
100 |
5.71 |
|
1.80 |
50 |
11.10 |
80 |
6.94 |
60 |
9.25 |
100 |
5.55 |
|
1.65 |
60 |
10.10 |
90 |
6.73 |
70 |
8.96 |
110 |
5.50 |
|
1.70 |
60 |
9.80 |
90 |
6.53 |
70 |
8.40 |
110 |
5.34 |
|
1.75 |
60 |
9.50 |
90 |
6.35 |
70 |
8.16 |
110 |
5.19 |
|
1.80 |
60 |
9.25 |
90 |
6.17 |
70 |
7.93 |
110 |
5.05 |
|
1.65 |
70 |
8.96 |
100 |
6.06 |
80 |
7.57 |
120 |
5.05 |
|
1.70 |
70 |
8.40 |
100 |
5.88 |
80 |
7.35 |
120 |
4.90 |
|
1.75 |
70 |
8.16 |
100 |
5.71 |
80 |
7.14 |
120 |
4.76 |
|
1.80 |
70 |
7.93 |
100 |
5.55 |
80 |
6.94 |
120 |
4.63 |
|
1.65 |
80 |
7.57 |
110 |
5.50 |
90 |
6.73 |
130 |
4.66 |
|
1.70 |
80 |
7.35 |
110 |
5.34 |
90 |
6.53 |
130 |
4.52 |
|
1.75 |
80 |
7.14 |
110 |
5.19 |
90 |
6.35 |
130 |
4.39 |
|
1.80 |
80 |
6.94 |
110 |
5.05 |
90 |
6.17 |
130 |
4.34 |
F. How much square meter, foot, inches metal to be coated: - The customer should calculate the used powder coverage in square meter, inches and foot per day after the one-day coating over. And keep a daily record of coverage.